symptoms of ketoacidosis in type 2 diabetes Ketoacidosis dka diabetic pathophysiology algorithm kussmaul acidosis grepmed hhs hyperosmolar hyperglycemic respiration dehydration hypotension acetone labored breathing tachycardia
If you or someone you know has diabetes, it’s important to understand the potential risks and complications that can arise. One such complication is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. DKA occurs when the body is unable to use glucose (sugar) for energy because there isn’t enough insulin available. This forces the body to break down fat for energy instead, which creates a buildup of acidic chemicals called ketones in the blood. This can lead to a dangerous condition called acidosis. But did you know that certain medications used to treat diabetes can also increase the risk of DKA? Specifically, medications known as SGLT2 inhibitors have been linked to a rare but serious form of DKA called euglycemic DKA. SGLT2 inhibitors work by blocking a protein called SGLT2, which is responsible for reabsorbing glucose in the kidneys. This leads to increased glucose excretion in the urine and lowers blood sugar levels. While these medications have been shown to be effective in treating type 2 diabetes, they can also cause a dangerous buildup of ketones in the blood. Symptoms of euglycemic DKA may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and confusion. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. To reduce your risk of developing euglycemic DKA while taking SGLT2 inhibitors, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have other risk factors such as a low-carbohydrate diet or excessive alcohol consumption. You should also be aware of the warning signs of DKA and seek medical attention if you experience them. If you have diabetes and are taking SGLT2 inhibitors, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about your risk of developing euglycemic DKA. They may recommend additional monitoring or switching to a different medication. Remember, managing your diabetes involves more than just taking medication. It’s also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and regular blood sugar monitoring. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can reduce your risk of complications and live a healthy and fulfilling life with diabetes.
If you are searching about Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments like What Is A Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Life Saving Info You Need To Read #, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual of Medicine and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual of Medicine. Here it is:
Diabetic Exchange: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatments
 diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
diabeticexchange.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type treatment mechanism ketosis vs symptoms nurse ketogenic sepsis notes signs sugar cancer body memory
Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
 zovon.comketoacidosis dka diabetic diagnosis breath
zovon.comketoacidosis dka diabetic diagnosis breath
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual Of Medicine
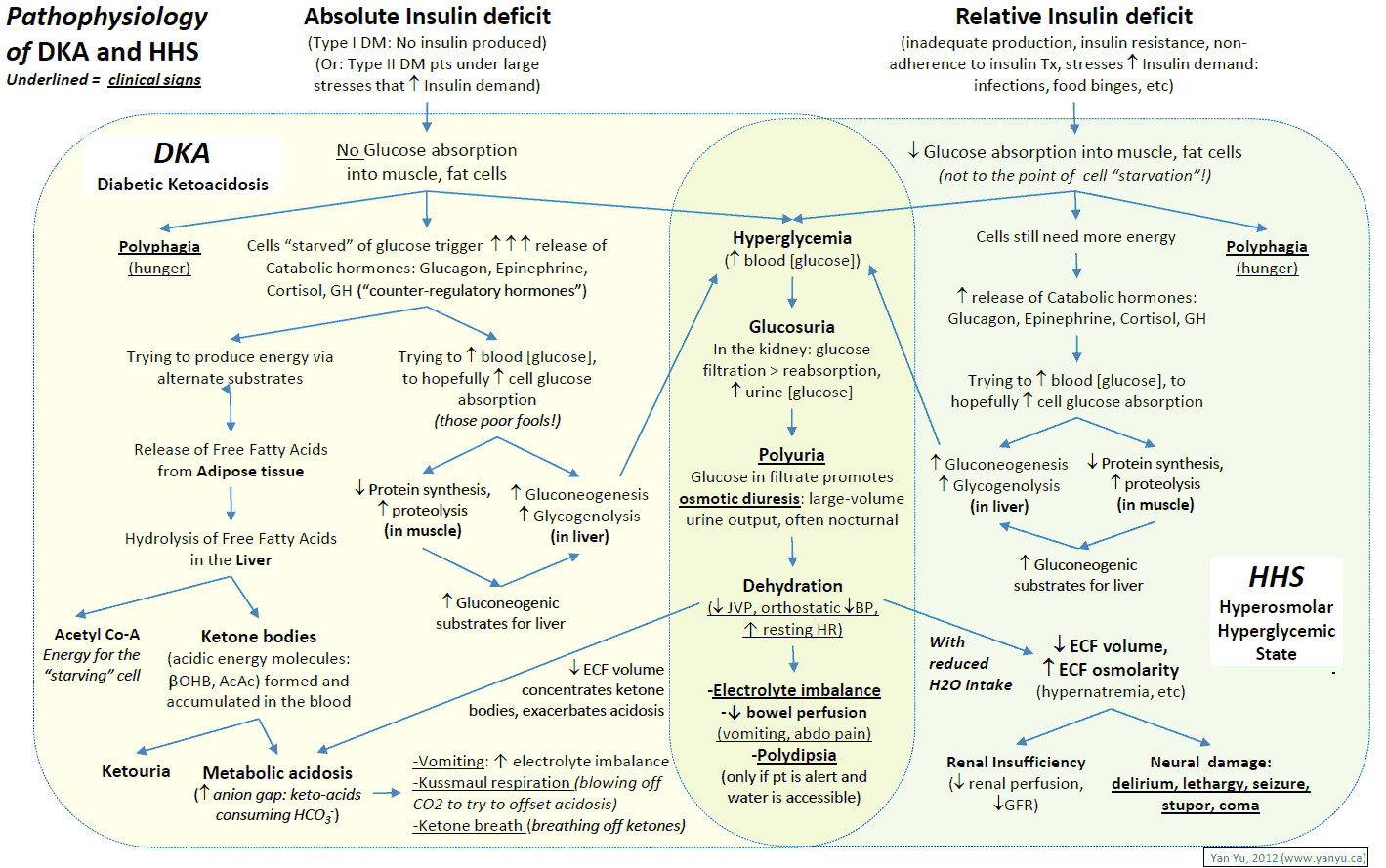 manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis dka diabetic pathophysiology algorithm kussmaul acidosis grepmed hhs hyperosmolar hyperglycemic respiration dehydration hypotension acetone labored breathing tachycardia
manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis dka diabetic pathophysiology algorithm kussmaul acidosis grepmed hhs hyperosmolar hyperglycemic respiration dehydration hypotension acetone labored breathing tachycardia
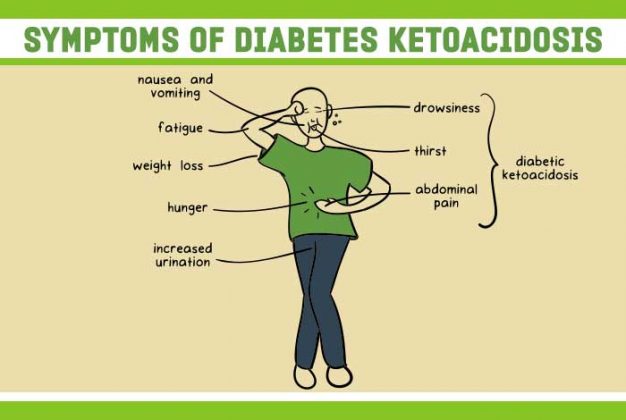
What Is A Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Life Saving Info You Need To Read #
 www.pinterest.comketoacidosis symptoms diabetic dka diabetes cetoacidosis invokana side causes coma
www.pinterest.comketoacidosis symptoms diabetic dka diabetes cetoacidosis invokana side causes coma
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
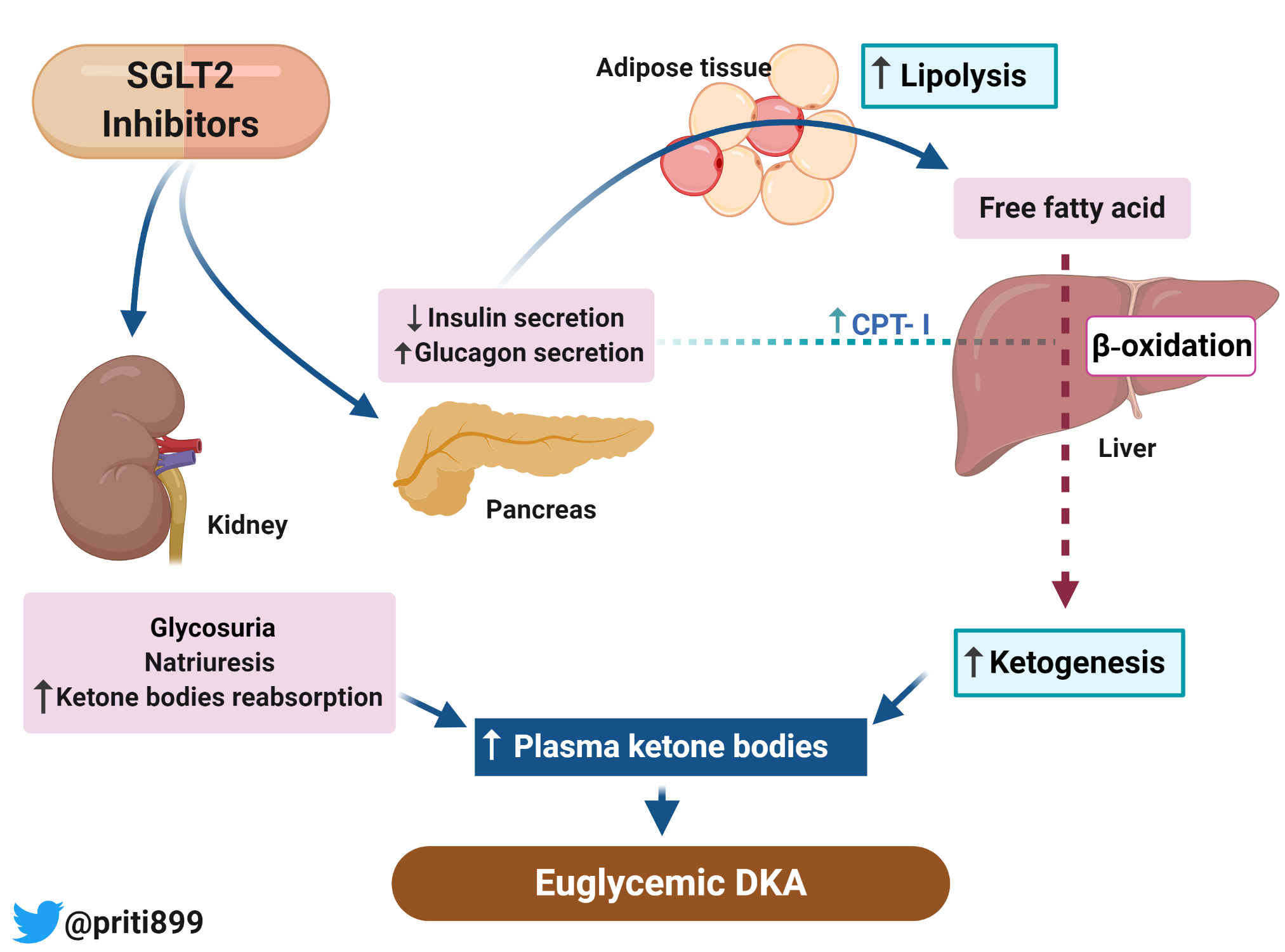 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Sglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. What is a diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow